Guide to pass AZ-900: Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
 |
| Pass AZ-900 certification exam |
I am working on Power BI for almost a year. With few use cases, I got exposure to Azure ecosystem and I was amused with the width of capabilities Azure ecosystem offers. I started with Microsoft defined learning paths.
I thought about completing Azure Fundamentals certification to enhance my knowledge of Azure. The content of Azure fundamentals is relevant for someone who would like to start their cloud journey on Microsoft Azure cloud and further strengthen the understanding of the service offerings, security, support, and infrastructure. Based on my experience, I would recommend to all aspirants creating a strategy on how to prepare and plan a timeline for the exam. A defined timeline helps in keeping us on track.
About AZ-900 Azure Fundamentals Certification
You can schedule the exam from https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/certifications/exams/az-900.
I suggest starting with free Microsoft eLearning module to have an overall understanding of the Azure system. The exam is categorized into four sections:
- Understand cloud concepts (15–20%)
- Understand core Azure services (30–35%)
- Understand security, privacy, compliance, and trust (25–30%)
- Understand Azure pricing and support (20–25%)
I prepared mostly from Microsoft learn modules and a few topics from Cloud Academy. While preparing for the exam, I have created very comprehensive notes from the aforementioned sites. I used these notes to do a quick review for the exam. These notes have a summary of all the required key concepts which will be very helpful in understanding the concepts and passing the exam.
Understand cloud concepts (20–25%)
Cloud Computing:
The delivery of computing services — including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence — over the Internet to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale.
Benefits of Cloud Computing:
- Cost -Cloud computing eliminates the capital expense of buying hardware and software and setting up and running on-site datacenters — the racks of servers, the round-the-clock electricity for power and cooling, and the IT experts for managing the infrastructure. It adds up fast.
- Speed -Most cloud computing services are provided self service and on demand, so even vast amounts of computing resources can be provisioned in minutes, typically with just a few mouse clicks, giving businesses a lot of flexibility and taking the pressure off capacity planning.
- Global scale -The benefits of cloud computing services include the ability to scale elastically. In cloud speak, that means delivering the right amount of IT resources — for example, more or less computing power, storage, bandwidth — right when they’re needed, and from the right geographic location.
- Productivity -On-site datacenters typically require a lot of “racking and stacking” — hardware setup, software patching, and other time-consuming IT management chores. Cloud computing removes the need for many of these tasks, so IT teams can spend time on achieving more important business goals.
- Performance -The biggest cloud computing services run on a worldwide network of secure datacenters, which are regularly upgraded to the latest generation of fast and efficient computing hardware. This offers several benefits over a single corporate datacenter, including reduced network latency for applications and greater economies of scale.
- Reliability -Cloud computing makes data backup, disaster recovery, and business continuity easier and less expensive because data can be mirrored at multiple redundant sites on the cloud provider’s network.
- Security -Many cloud providers offer a broad set of policies, technologies, and controls that strengthen your security posture overall, helping protect your data, apps, and infrastructure from potential threats.
- High Availability -Refers to a set of technologies that minimize IT disruptions by providing business continuity of IT services through redundant, fault-tolerant, or failover-protected components inside the same data center.
- Scalability -Ability to increase the resources based on the requirements of the solution.
- Elasticity -Ability to quickly expand or decrease computer processing, memory, and storage resources to meet changing demands without worrying.
- Agility -Quickly adapting to meet customer needs.
- Fault Tolerance -Ability to remain operational when few services fails.
- Disaster Recovery -Refers to the minimizing of IT services disruption and their recovery, process of restoring application functionality in the wake of a catastrophic loss.
- Understand the principles of economies of scale -Ability to do things more efficiently or at a lower-cost per unit when operating at a larger scale.
CapEx vs OpEx:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): CapEx is the spending of money on physical infrastructure up front, and then deducting that expense from your tax bill over time. CapEx is an upfront cost, which has a value that reduces over time.
- Operational Expenditure (OpEx): OpEx is spending money on services or products now and being billed for them now. You can deduct this expense from your tax bill in the same year. There’s no upfront cost. You pay for a service or product as you use it.
Types of cloud services:
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) -Infrastructure as a Service is the most flexible category of cloud services. It aims to give you the most control over the provided hardware that runs your application (IT infrastructure servers and virtual machines (VMs), storage, and operating systems). Instead of buying hardware, with IaaS, you rent it. It’s an instant computing infrastructure, provisioned and managed over the internet.
- Platform as a service (PaaS) -PaaS provides an environment for building, testing, and deploying software applications. The goal of PaaS is to help you create an application quickly without managing the underlying infrastructure. For example, when deploying a web application using PaaS, you don’t have to install an operating system, web server, or even system updates. PaaS is a complete development and deployment environment in the cloud, with resources that enable organizations to deliver everything from simple cloud-based apps to sophisticated cloud-enabled enterprise applications. Resources are purchased from a cloud service provider on a pay-as-you-go basis and accessed over a secure Internet connection.
- Software as a service (SaaS) -SaaS is software that is centrally hosted and managed for the end customer. It is usually based on an architecture where one version of the application is used for all customers, and licensed through a monthly or annual subscription. Office 365, Skype, and Dynamics CRM Online are perfect examples of SaaS software.
Cloud deployment models:
- Public Cloud:This is the most common deployment model. In this case, you have no local hardware to manage or keep up-to-date — everything runs on your cloud provider’s hardware. In some cases, you can save additional costs by sharing computing resources with other cloud users.
Businesses can use multiple public cloud providers of varying scale. Microsoft Azure is an example of a public cloud provider. - Private cloud:You create a cloud environment in your own datacenter and provide self-service access to compute resources to users in your organization. This offers a simulation of a public cloud to your users, but you remain completely responsible for the purchase and maintenance of the hardware and software services you provide.
- Hybrid cloud:Combines public and private clouds, allowing you to run your applications in the most appropriate location. For example, you could host a website in the public cloud and link it to a highly secure database hosted in your private cloud (or on-premises datacenter).
Microsoft Cloud Adoption Framework for Azure:
The Microsoft Cloud Adoption Framework for Azure is proven guidance that’s designed to help you create and implement the business and technology strategies necessary for your organization to succeed in the cloud. It provides best practices, documentation, and tools that cloud architects, IT professionals, and business decision makers need to successfully achieve their short- and long-term objectives.
By using the Microsoft Cloud Adoption Framework for Azure best practices, organizations can better align their business and technical strategies to ensure success.
- Realize your business objectives - Identify opportunities for your organization in the cloud and realize your objectives using cloud technology.
- Prepare your organization for the cloud - Identify productive and sustainable ways to help your organization understand and embrace technology changes that will improve business outcomes.
- Migrate to the cloud and optimize - Move your digital assets to the cloud and then optimize them—and your operational processes—for excellence with innovative cloud-based technologies.
Shared responsibility in the cloud:
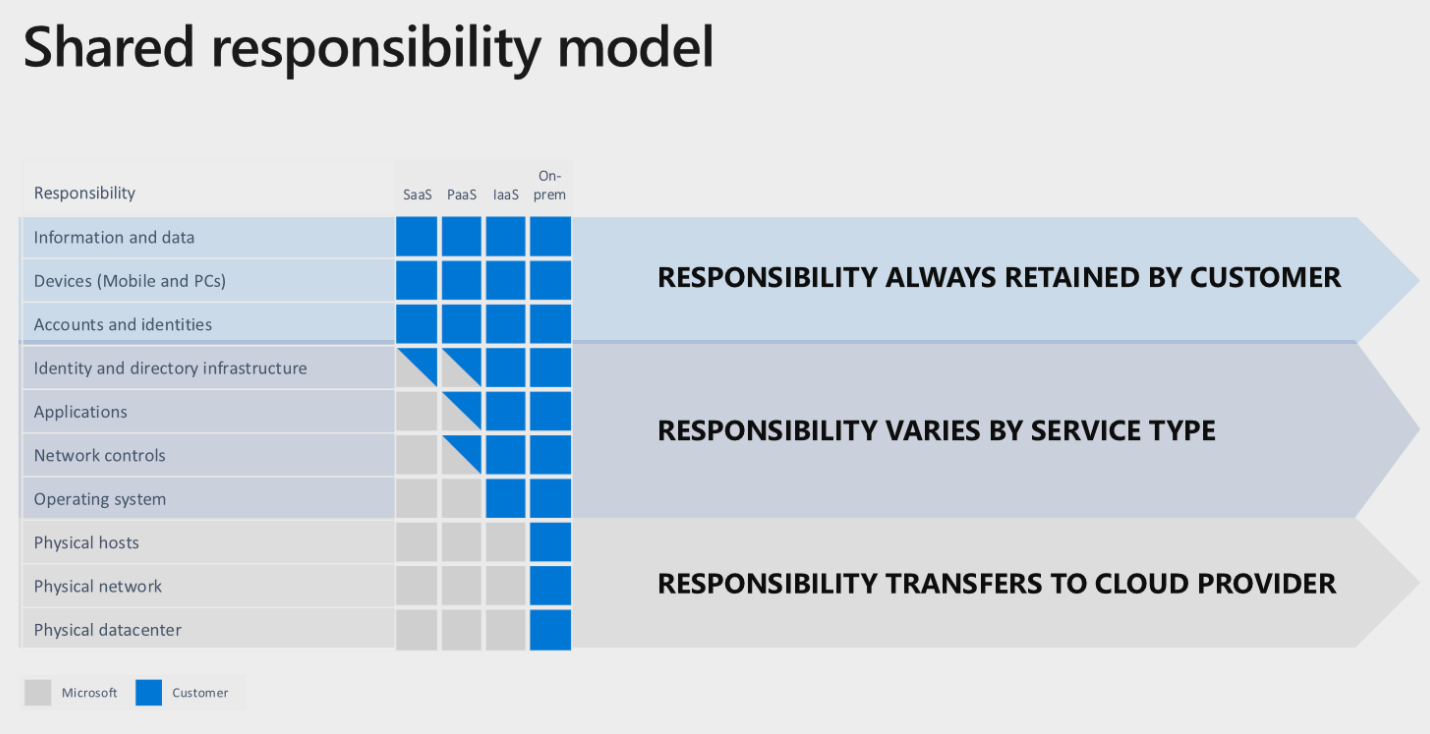
Understand core Azure services (30–35%):
Regions:
Region is a set of datacenters deployed within a latency-defined perimeter and connected through a dedicated regional low-latency network.
With more global regions than any other cloud provider, Azure gives customers the flexibility to deploy applications where they need to. Azure is generally available in 53 regions around the world, with plans announced for 5 additional regions.
Azure global infrastructure:
Achieve global reach and the local presence you need with Azure’s global presence. Go beyond the limits of your on-premises datacenter using the scalable, trusted, and reliable Microsoft Cloud. Transform your business and reduce costs with an energy-efficient infrastructure spanning more than 100 highly secure facilities worldwide, linked by one of the largest networks on earth.
- 58 Azure regions
- Available in 140 countries
- Up to 1.6 Pbps of bandwidth in a region
Availability Zones:
Availability Zones are physically separate locations within an Azure region. Each Availability Zone is made up of one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking.
Availability Zones allow customers to run mission-critical applications with high availability and low-latency replication.
Geographies:
A geography is a discrete market, typically containing two or more regions, that preserves data residency and compliance boundaries. Geographies allow customers with specific data-residency and compliance needs to keep their data and applications close. Geographies are fault-tolerant to withstand complete region failure through their connection to our dedicated high-capacity networking infrastructure.
Resource Groups:
- All the resources in your group should share the same lifecycle. You deploy, update, and delete them together. If one resource, such as a database server, needs to exist on a different deployment cycle it should be in another resource group.
- Each resource can only exist in one resource group.
- Some resources can exist outside of a resource group. These resources are deployed to the subscription, management group, or tenant. Only specific resource types are supported at these scopes.
- You can add or remove a resource to a resource group at any time.
- You can move a resource from one resource group to another group.
- A resource group can contain resources that are located in different regions.
- A resource group can be used to scope access control for administrative actions.
- A resource can interact with resources in other resource groups. This interaction is common when the two resources are related but don’t share the same lifecycle (for example, web apps connecting to a database).
Azure Resource Manager
Azure Resource Manager is the deployment and management service for Azure. It provides a management layer that enables you to create, update, and delete resources in your Azure account. You use management features, like access control, locks, and tags, to secure and organize your resources after deployment.
Benefits of using Resource Manager:
- Manage your infrastructure through declarative templates rather than scripts.
- Deploy, manage, and monitor all the resources for your solution as a group, rather than handling these resources individually.
- Redeploy your solution throughout the development lifecycle and have confidence your resources are deployed in a consistent state.
- Define the dependencies between resources so they’re deployed in the correct order.
- Apply access control to all services because Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is natively integrated into the management platform.
- Apply tags to resources to logically organize all the resources in your subscription.
- Clarify your organization’s billing by viewing costs for a group of resources sharing the same tag.
Azure products for Compute:
- Virtual Machines:Azure Virtual Machines (VM) is one of several types of on-demand, scalable computing resources that Azure offers. Typically, you choose a VM when you need more control over the computing environment than the other choices offer. This article gives you information about what you should consider before you create a VM, how you create it, and how you manage it.An Azure VM gives you the flexibility of virtualization without having to buy and maintain the physical hardware that runs it. However, you still need to maintain the VM by performing tasks, such as configuring, patching, and installing the software that runs on it.
- Virtual Machine Scale Sets:Azure virtual machine scale sets let you create and manage a group of identical, load balanced VMs. The number of VM instances can automatically increase or decrease in response to demand or a defined schedule. Scale sets provide high availability to your applications, and allow you to centrally manage, configure, and update a large number of VMs. With virtual machine scale sets, you can build large-scale services for areas such as compute, big data, and container workloads.
- App Service Functions:Azure App Service enables you to quickly build, deploy, and scale enterprise-grade web and API apps. Applications and services deployed on App Service can meet rigorous performance, scalability, and security requirements.
- Azure Container Instances (ACI):Use Azure Container Instances for data processing where source data is ingested, processed, and placed in a durable store such as Azure Blob storage. By processing the data with ACI rather than statically-provisioned virtual machines, you can achieve significant cost savings through per-second billing.
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS):Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) makes it simple to deploy a managed Kubernetes cluster in Azure. AKS reduces the complexity and operational overhead of managing Kubernetes by offloading much of that responsibility to Azure. As a hosted Kubernetes service, Azure handles critical tasks like health monitoring and maintenance for you. The Kubernetes masters are managed by Azure. You only manage and maintain the agent nodes. As a managed Kubernetes service, AKS is free - you only pay for the agent nodes within your clusters, not for the masters.
Azure products for Networking:
- Virtual Network:Azure Virtual Network (VNet) is the fundamental building block for your private network in Azure. VNet enables many types of Azure resources, such as Azure Virtual Machines (VM), to securely communicate with each other, the internet, and on-premises networks. VNet is similar to a traditional network that you'd operate in your own data center, but brings with it additional benefits of Azure's infrastructure such as scale, availability, and isolation.
- Load Balancer:An Azure load balancer is a Layer-4 (TCP, UDP) load balancer that provides high availability by distributing incoming traffic among healthy VMs. A load balancer health probe monitors a given port on each VM and only distributes traffic to an operational VM.
Virtual machines connect to a load balancer using their virtual network interface card (NIC). To distribute traffic to the VMs, a back-end address pool contains the IP addresses of the virtual (NICs) connected to the load balancer. - VPN Gateway:A VPN gateway is a specific type of virtual network gateway that is used to send encrypted traffic between an Azure virtual network and an on-premises location over the public Internet. You can also use a VPN gateway to send encrypted traffic between Azure virtual networks over the Microsoft network. Each virtual network can have only one VPN gateway. However, you can create multiple connections to the same VPN gateway. When you create multiple connections to the same VPN gateway, all VPN tunnels share the available gateway bandwidth.
- Application Gateway:Azure Application Gateway is a web traffic load balancer that enables you to manage traffic to your web applications. Traditional load balancers operate at the transport layer (OSI layer 4 - TCP and UDP) and route traffic based on source IP address and port, to a destination IP address and port.Application Gateway can make routing decisions based on additional attributes of an HTTP request, for example URI path or host headers. For example, you can route traffic based on the incoming URL. So if /images is in the incoming URL, you can route traffic to a specific set of servers (known as a pool) configured for images. If /video is in the URL, that traffic is routed to another pool that's optimized for videos.
- Content Delivery Network:Azure Content Delivery Network (CDN) lets you reduce load times, save bandwidth, and speed responsiveness—whether you’re developing or managing websites or mobile apps, or encoding and distributing streaming media, gaming software, firmware updates, or IoT endpoints.
Azure products for Storage:
- Blob Storage:Azure Blob Storage helps you create data lakes for your analytics needs, and provides storage to build powerful cloud-native and mobile apps. Optimize costs with tiered storage for your long-term data, and flexibly scale up for high-performance computing and machine learning workloads.
- Sixteen nines of designed durability with geo-replication and flexibility to scale as needed
- Authentication with Azure Active Directory and role-based access control (RBAC), plus encryption at rest and advanced threat protection
- File namespace and multi-protocol access support enabling analytics workloads for data insights
- End-to-end lifecycle management, policy-based access control, and immutable (WORM) storage
- Disk Storage:Persistent and high-performing disks for Azure Virtual Machines.
Get the durability, scalability, availability, and security you need for all of your data—from test scenarios to mission-critical workloads. Use Azure Ultra Disk Storage when you need sub-millisecond latency and extremely scalable performance, Azure Premium SSD for production workloads, and Azure Standard SSD for cost-effective and consistent performance. - Automatic disk creation and management—simply select the disk type and size needed
- Create thousands of managed disks simultaneously in minutes with a single subscription
- Data encrypted at rest by default with Microsoft & Customer Managed Key options
- 99.999-percent availability and consistent enterprise-grade durability
- File Storage:Azure File Storage allows applications to mount file shares from anywhere in the world, your on-premises applications can take advantage of cloud storage without change. Azure File Storage also implements REST API protocol, which enables you to develop modern applications that integrate with existing applications.
- Archive Storage:Azure Archive Storage offers low-cost, durable, and highly available secure cloud storage for rarely accessed data with flexible latency requirements. Store terabytes of data in the cloud for only a few dollars a month, and repurpose your storage infrastructure for other critical business objectives.
Azure products for Databases:
- Cosmos DB:Azure Cosmos DB is Microsoft’s globally distributed, multi-model database service for operational and analytics workloads. It offers multi-mastering feature by automatically scaling throughput, compute, and storage.
- Azure SQL Database:Azure SQL Database is a fully managed Platform as a Service (PaaS) Database Engine that handles most of the database management functions such as upgrading, patching, backups, and monitoring without user involvement. Azure SQL Database is always running on the latest stable version of SQL Server Database Engine and patched OS with 99.99% availability. PaaS capabilities that are built into Azure SQL Database enables you to focus on the domain-specific database administration and optimization activities that are critical for your business.
- Azure Database for MySQL:Azure Database for MySQL is a relational database service in the Microsoft cloud based on the MySQL Community Edition (available under the GPLv2 license) database engine, versions 5.6, 5.7, and 8.0. Azure Database for MySQL delivers:Built-in high availability with no additional cost.
- Predictable performance, using inclusive pay-as-you-go pricing.
- Scale as needed within seconds.
- Secured to protect sensitive data at-rest and in-motion.
- Automatic backups and point-in-time-restore for up to 35 days.
- Enterprise-grade security and compliance.
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL:Azure Database for PostgreSQL is a relational database service based on the open-source Postgres database engine. It's a fully managed database-as-a-service offering that can handle mission-critical workloads with predictable performance, security, high availability, and dynamic scalability. It's available in two deployment options, as a single server and as a Hyperscale (Citus) cluster. The Hyperscale (Citus) option horizontally scales queries across multiple machines using sharding, and serves applications that require greater scale and performance.
- Azure Database Migration service:Azure Database Migration Service is a tool that helps you simplify, guide, and automate your database migration to Azure. Easily migrate your data, schema, and objects from multiple sources to the cloud at scale.
- Database-sensitive migration moves data, schema, and objects to Azure
- Easy-to-understand process helps you get the job done right the first time
- Supports Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and Oracle migration to Azure from on-premises and other clouds
- Highly resilient and self-healing migration service provides reliable outcomes with near-zero downtime
Azure Marketplace:
An online marketplace for applications and services that lets businesses of all sizes offer solutions to customers around the world.
Internet of Things (IoT):
- Azure IoT Hub:Azure IoT Hub provides a cloud-hosted solution backend to connect virtually any device. Extend your solution from the cloud to the edge with per-device authentication, built-in device management, and scaled provisioning.
- Security-enhanced communication channel for sending and receiving data from IoT devices
- Built-in device management and provisioning to connect and manage IoT devices at scale
- Full integration with Event Grid and serverless compute, simplifying IoT application development
- Compatibility with Azure IoT Edge for building hybrid IoT applications
- Azure IoT Central:IoT Central is an IoT application platform that reduces the burden and cost of developing, managing, and maintaining enterprise-grade IoT solutions. Choosing to build with IoT Central gives you the opportunity to focus time, money, and energy on transforming your business with IoT data, rather than just maintaining and updating a complex and continually evolving IoT infrastructure.The web UI lets you monitor device conditions, create rules, and manage millions of devices and their data throughout their life cycle. Furthermore, it enables you to act on device insights by extending IoT intelligence into line-of-business applications.
Big Data and Analytics:
- Azure SQL Data Warehouse:A cloud based SQL data warehouse offered as PaaS.
- Azure HDInsight:Azure HDInsight is a managed, full-spectrum, open-source analytics service in the cloud for enterprises. You can use open-source frameworks such as Hadoop, Apache Spark, Apache Hive, LLAP, Apache Kafka, Apache Storm, R, and more.
- Azure Databricks:Azure Databricks is a fast, easy, and collaborative Apache Spark-based big data analytics service designed for data science and data engineering.
- Azure Machine Learning Service and Studio:Azure Machine Learning can be used for any kind of machine learning, from classical ml to deep learning, supervised, and unsupervised learning. Whether you prefer to write Python or R code or zero-code/low-code options such as the designer, you can build, train, and track highly accurate machine learning and deep-learning models in an Azure Machine Learning Workspace.
Containers:
Containers provide a consistent, isolated execution environment for applications. They’re similar to VMs except they don’t require a guest operating system. Instead, the application and all its dependencies is packaged into a “container” and then a standard runtime environment is used to execute the app. This allows the container to start up in just a few seconds, because there’s no OS to boot and initialize. You only need the app to launch.
Serverless computing :
Lets you run application code without creating, configuring, or maintaining a server. The core idea is that your application is broken into separate functions that run when triggered by some action. This is ideal for automated tasks — for example, you can build a serverless process that automatically sends an email confirmation after a customer makes an online purchase.
The serverless model differs from VMs and containers in that you only pay for the processing time used by each function as it executes. VMs and containers are charged while they’re running — even if the applications on them are idle. This architecture doesn’t work for every app — but when the app logic can be separated to independent units, you can test them separately, update them separately, and launch them in microseconds, making this approach the fastest option for deployment.
- Azure Functions - Azure Functions is a serverless compute service that lets you run event-triggered code without having to explicitly provision or manage infrastructure.
- Logic Apps - Build automated scalable workflows, business processes, and enterprise orchestrations to integrate your apps and data across cloud services and on-premises systems.
- Event Grid - Azure Event Grid allows you to easily build applications with event-based architectures. First, select the Azure resource you would like to subscribe to, and then give the event handler or WebHook endpoint to send the event to. Event Grid has built-in support for events coming from Azure services, like storage blobs and resource groups. Event Grid also has support for your own events, using custom topics.
DevOps solutions:
Provides version control, reporting, requirements management, project management, automated builds, lab management, testing and release management capabilities.
- Azure DevOps:
- An end to end tool options for developing and deploying solutions.
- Azure DevTest Labs:
- Fast, easy and lean dev test environments
- Quickly provision development and test environments
- Minimize waste with quotas and policies
- Set automated shutdowns to minimize costs
- Build Windows and Linux environments
- Explore an application centric approach to dynamically create and manage complex, cloud-native applications in Azure using Quali’s CloudShell Colony
Azure Portal:
A web-based, unified console that provides an alternative to command-line tools. With the Azure portal, you can manage your Azure subscription using a graphical user interface. You can build, manage, and monitor everything from simple web apps to complex cloud deployments.
Azure PowerShell:
Azure PowerShell is a set of cmdlets for managing Azure resources directly from the PowerShell command line. Azure PowerShell is designed to make it easy to learn and get started with, but provides powerful features for automation. Written in .NET Standard, Azure PowerShell works with PowerShell 5.1 on Windows, and PowerShell 6.x and higher on all platforms.
Azure CLI:
The Azure command-line interface (Azure CLI) is a set of commands used to create and manage Azure resources. The Azure CLI is available across Azure services and is designed to get you working quickly with Azure, with an emphasis on automation.
Azure Cloud Shell:
Azure Cloud Shell is an interactive, authenticated, browser-accessible shell for managing Azure resources. It provides the flexibility of choosing the shell experience that best suits the way you work, either Bash or PowerShell.
Azure Status:
The Azure status page is a global view of the health of all Azure services in all regions. It's a quick reference for incidents with widespread impact. With Azure status, you can get information on service availability. Azure status is available to everyone to view all services that report their service health, as well as incidents with wide-ranging impact.
Azure Resource Health:
Azure Resource Health helps you diagnose and get support for service problems that affect your Azure resources. It reports on the current and past health of your resources. Resource Health gives you a personalized dashboard of the health of your resources. Resource Health shows all the times that your resources have been unavailable because of Azure service problems. This data makes it easy for you to see if an SLA was violated.
Using business metrics to design resilient Azure applications:
- Workload availability targets
- Consider cost and complexity
- Identify dependencies
- Recovery metrics
- Recovery time objective (RTO) - maximum acceptable time an application is unavailable after an incident.
- Recovery point objective (RPO) - maximum duration of data loss that's acceptable during a disaster.
- Availability metrics
- Mean time to recover (MTTR) - average time it takes to restore a component after a failure.
- Mean time between failures (MTBF) - how long a component can reasonably expect to last between outages.
Understand security, privacy, compliance, and trust (25–30%):
Network Security Groups (NSG):
Azure network security group to filter network traffic to and from Azure resources in an Azure virtual network. A network security group contains security rules that allow or deny inbound network traffic to, or outbound network traffic from, several types of Azure resources. For each rule, you can specify source and destination, port, and protocol.
Application Security Groups (ASG):
Application security groups enable you to configure network security as a natural extension of an application's structure, allowing you to group virtual machines and define network security policies based on those groups. You can reuse your security policy at scale without manual maintenance of explicit IP addresses. The platform handles the complexity of explicit IP addresses and multiple rule sets, allowing you to focus on your business logic.
Azure Firewall:Cloud-native network security to protect your Azure Virtual Network resources
- Stateful firewall as a service
- Built-in high availability with unrestricted cloud scalability
- Ability to centrally create, enforce, and log application and network connectivity policies
- Threat intelligence-based filtering
- Source and destination Network Address Translation (SNAT and DNAT) support
- Fully integrated with Azure Monitor for logging and analytics
- Support for hybrid connectivity through deployment behind VPN and ExpressRoute Gateways
Azure DDoS Protection:
Protect your Azure resources from Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks
- Always-on monitoring and automatic network attack mitigation
- Adaptive tuning based on platform insights in Azure
- Application layer protection with Azure Application Gateway Web Application Firewall
- Integration with Azure Monitor for analytics and insights
- Protection against the unforeseen costs of a DDoS attack
Azure Monitor:
Full observability into your applications, infrastructure, and network
- Store and analyze all your operational telemetry in a centralized, fully managed, scalable data store that’s optimized for performance and cost.
- Test your hypotheses and reveal hidden patterns using the advanced analytic engine, interactive query language, and built-in machine learning constructs.
- Integrate with popular DevOps, issue management, IT service management, and security information and event management tools.
Azure Security Center:
Azure Security Center is a unified infrastructure security management system that strengthens the security posture of your data centers, and provides advanced threat protection across your hybrid workloads in the cloud - whether they're in Azure or not - as well as on premises.
Keeping your resources safe is a joint effort between your cloud provider, Azure, and you, the customer. You have to make sure your workloads are secure as you move to the cloud, and at the same time, when you move to IaaS (infrastructure as a service) there is more customer responsibility than there was in PaaS (platform as a service), and SaaS (software as a service). Azure Security Center provides you the tools needed to harden your network, secure your services and make sure you're on top of your security posture.
Azure Security Center addresses the three most urgent security challenges:
- Rapidly changing workloads – It's both a strength and a challenge of the cloud. On the one hand, end users are empowered to do more. On the other, how do you make sure that the ever-changing services people are using and creating are up to your security standards and follow security best practices?
- Increasingly sophisticated attacks - Wherever you run your workloads, the attacks keep getting more sophisticated. You have to secure your public cloud workloads, which are, in effect, an Internet facing workload that can leave you even more vulnerable if you don't follow security best practices.
- Security skills are in short supply - The number of security alerts and alerting systems far outnumbers the number of administrators with the necessary background and experience to make sure your environments are protected. Staying up-to-date with the latest attacks is a constant challenge, making it impossible to stay in place while the world of security is an ever-changing front.
To help you protect yourself against these challenges, Security Center provides you with the tools to:
- Strengthen security posture: Security Center assesses your environment and enables you to understand the status of your resources, and whether they are secure.
- Protect against threats: Security Center assesses your workloads and raises threat prevention recommendations and security alerts.
- Get secure faster: In Security Center, everything is done in cloud speed. Because it is natively integrated, deployment of Security Center is easy, providing you with auto-provisioning and protection with Azure services.
Authentication and Authorization:
- With authentication, the system proves that you are who you say you are.
- With authorization, the system verifies that you have rights to do what you want to do.
Azure Active Directory:
enterprise identity service provides single sign-on and multi-factor authentication to help protect your users from 99.9 percent of cybersecurity attacks.
- Single sign-on simplifies access to your apps from anywhere
- Conditional Access and multi-factor authentication help protect and govern access
- A single identity platform lets you engage with internal and external users more securely
- Developer tools make it easy to integrate identity into your apps and services
Azure Multi-Factor Authentication:
Azure Multi-Factor Authentication works by requiring two or more of the following authentication methods:
- Something you know, typically a password.
- Something you have, such as a trusted device that is not easily duplicated, like a phone or hardware key.
- Something you are - biometrics like a fingerprint or face scan.
Azure RBAC:
It helps you manage who has access to Azure resources, what they can do with those resources, and what areas they have access to. Azure RBAC is an authorization system built on Azure Resource Manager that provides fine-grained access management of Azure resources.
- Allow one user to manage virtual machines in a subscription and another user to manage virtual networks
- Allow a DBA group to manage SQL databases in a subscription
- Allow a user to manage all resources in a resource group, such as virtual machines, websites, and subnets
- Allow an application to access all resources in a resource group
Key Vault:
Safeguard cryptographic keys and other secrets used by cloud apps and services
- Increase security and control over keys and passwords
- Create and import encryption keys in minutes
- Applications have no direct access to keys
- Use FIPS 140-2 Level 2 validated HSMs
- Reduce latency with cloud scale and global redundancy
- Simplify and automate tasks for SSL/TLS certificates
Benefits of Key Vault:
- Enhance data protection and compliance - Secure key management is essential to protect data in the cloud. Use Azure Key Vault to encrypt keys and small secrets like passwords that use keys stored in hardware security modules (HSMs). For more assurance, import or generate keys in HSMs, and Microsoft processes your keys in FIPS 140-2 Level 2 validated HSMs (hardware and firmware). With Key Vault, Microsoft doesn’t see or extract your keys. Monitor and audit your key use with Azure logging—pipe logs into Azure HDInsight or your security information and event management (SIEM) solution for more analysis and threat detection.
- All of the control, none of the work - Use Key Vault and you don’t need to provision, configure, patch, and maintain HSMs and key management software. Provision new vaults and keys (or import keys from your own HSMs) in minutes and centrally manage keys, secrets, and policies. You keep control over your keys—simply grant permission for your own and partner applications to use them as needed. Applications never have direct access to keys.
- Boost performance and achieve global scale - Improve performance and reduce the latency of your cloud applications by storing cryptographic keys in the cloud, instead of on-premises. Key Vault quickly scales to meet the cryptographic needs of your cloud applications and match peak demand, without the cost of deploying dedicated HSMs. Achieve global redundancy by provisioning vaults in Azure global datacenters—keep a copy in your own HSMs for more durability.
Azure Advanced Threat Protection (ATP):
Detect and investigate advanced attacks on-premises and in the cloud
- Identify suspicious user and device activity with both known-technique detection and behavioral analytics
- Analyze threat intelligence from the cloud and on-premises
- Protect user identities and credentials stored in Active Directory
- View clear attack information on a simple timeline for fast triage
- Monitor multiple entry points through integration with Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection
Azure Governance:
Take advantage of built-in and custom policies to set guardrails in your subscriptions. Easily deploy fully governed environments throughout your organization with Azure Blueprints. And, manage costs by gaining insights into your cloud spend so that you get the most from your cloud investments.
- Enforce and audit your policies for any Azure service
- Create compliant environments using Azure Blueprints, including resources, policies, and role-access controls
- Ensure that you’re compliant with external regulations by using built-in compliance controls
- Monitor spend and encourage accountability across your entire organization
Azure Policy:
Reduce the time needed to audit your environments by having all your compliance data in a single place. Set guardrails throughout your resources to help ensure cloud compliance and avoid misconfigurations. Reduce the number of external approval processes by implementing policies at the core of the Azure platform for increased developer productivity. Control and optimize your cloud spend to get more value from your investment.
- Real-time policy enforcement and evaluation
- Cloud policy management and security at scale
- Automated remediation of existing resources at scale
- Comprehensive compliance view of all your resources
Management Groups:
Management Groups are containers that help you manage access, policy, and compliance across multiple subscriptions. You can create these containers to build an effective and efficient hierarchy that can be used with Azure Policy and Azure Role Based Access Controls.
Resource Locks:
As an administrator, you may need to lock a subscription, resource group, or resource to prevent other users in your organization from accidentally deleting or modifying critical resources. You can set the lock level to CanNotDelete or ReadOnly. In the portal, the locks are called Delete and Read-only respectively.
- CanNotDelete means authorized users can still read and modify a resource, but they can't delete the resource.
- ReadOnly means authorized users can read a resource, but they can't delete or update the resource. Applying this lock is similar to restricting all authorized users to the permissions granted by the Reader role.
Azure Blueprints:
Azure Blueprints enables cloud architects and central information technology groups to define a repeatable set of Azure resources that implements and adheres to an organization's standards, patterns, and requirements. Azure Blueprints makes it possible for development teams to rapidly build and stand up new environments with trust they're building within organizational compliance with a set of built-in components, such as networking, to speed up development and delivery.
Blueprints are a declarative way to orchestrate the deployment of various resource templates and other artifacts such as:
- Role Assignments
- Policy Assignments
- Azure Resource Manager templates
- Resource Groups
Azure Service Health:
Azure Service Health notifies you about Azure service incidents and planned maintenance so you can take action to mitigate downtime. Configure customizable cloud alerts and use your personalized dashboard to analyze health issues, monitor the impact to your cloud resources, get guidance and support, and share details and updates.
- Personalized dashboard shows the service issues that affect you
- Configurable cloud alerts notify you about active and upcoming service issues
- Shareable details and updates, including incident root cause analyses
- Guidance and support during service incidents
Service Health tracks four types of health events that may impact your resources:
- Service issues - Problems in the Azure services that affect you right now.
- Planned maintenance - Upcoming maintenance that can affect the availability of your services in the future.
- Health advisories - Changes in Azure services that require your attention. Examples include deprecation of Azure features or upgrade requirements (e.g upgrade to a supported PHP framework).
- Security advisories (preview) - Security related notifications that may affect the availability of your Azure services.
Azure data privacy and protection:
Automate your data privacy, inspire customer trust, and feel confident building solutions that analyze sensitive data on Microsoft Azure—the cloud platform that adheres to some of the world’s strictest privacy standards.
- Microsoft Azure Information Protection—to configure policies to classify, label, and help protect data based on its sensitivity. Control and help secure email, documents, and sensitive data that you share outside your company. From easy classification to embedded labels and permissions, enhance data protection at all times with Azure Information Protection—no matter where it’s stored or who it’s shared with.
- Azure Policy—to define and enforce policies that help your cloud environment become compliant with internal policies and external regulations.
- Data subject requests—to get help fulfilling your General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) requests. A formal request by a data subject to a controller to take an action on their personal data is called a DSR.
- Compliance Manager—to use a dashboard to track how well you’re adhering to ISO 2700 and GDPR controls for Office 365 and Azure.
GDPR:
European Union (EU) data protection and privacy law. The GDPR imposes rules on companies, government agencies, non-profits, and other organizations that offer goods and services to people in the EU, or that collect and analyze data tied to EU residents.
ISO:
International Organization for Standardization
NIST:
National Institute of Standards and Technology
Microsoft Privacy Statement:
Explains what personal data Microsoft collects and how the company uses it.
Trust center:
It provides information on security, privacy, and compliance topics for customers of Azure and other Microsoft Online Services.
Service Trust Portal:
It is a companion feature to the Trust Center that provides access to audit reports, GDPR documentation, compliance guides, and related documents that provide more detailed information on how Microsoft helps protect your data.
Azure Government cloud services:
Unparalleled flexibility and breakthrough innovation for US government agencies and their partners
- Get world-class security, protection, and compliance
- Modernize your legacy infrastructure to a flexible, hybrid environment
- Give your workloads capacity when and where you need it
- Gain efficiencies and cost savings across departments
Who can use this:
Below governments and their partners-
- Federal Agencies
- State and local agencies
- US Department of Defense
- National Security
Understand Azure pricing and support (20–25%):
Azure subscriptions:
Azure subscription is associated with specific accounts. There are three types of subscriptions:
Factors affecting costs:
- Resource type
- Services
- Location
- Azure billing zones
- Egress traffic
Ingress Traffic:
Ingress traffic is inbound traffic to Azure and is free.
Egress Traffic:
Egress traffic is outbound traffic from Azure and is charged.
Save on infrastructure costs:
- Use Azure credits
- Use spending limits
- Use reserved instances
- Choose low-cost locations and regions
- Research available cost-saving offers
- Right-size underutilized virtual machines
- Deallocate virtual machines in off hours
- Delete unused virtual machines
- Migrate to PaaS or SaaS services
Save on licensing costs:
- Linux vs. Windows
- Azure Hybrid Benefit for Windows Server
- Azure Hybrid Benefit for SQL Server
- Use Dev/Test subscription offers
- Bring your own SQL Server license
- Use SQL Server Developer Edition
Pricing calculator:
Configure and estimate the costs for Azure products
Option
|
Description
|
Region
|
Lists the regions from which you can provision a product. Southeast Asia, central Canada, the western United States, and northern Europe are among the possible regions available for some resources.
|
Tier
|
Sets the type of tier you wish to allocate to a selected resource, such as Free Tier, Basic Tier, etc.
|
Billing Options
|
Highlights the billing options available to different types of customers and subscriptions for a chosen product.
|
Support Options
|
Allows you to pick from included or paid support pricing options for a selected product.
|
Programs and Offers
|
Allows you to choose from available price offerings according to your customer or subscription type.
|
Azure Dev/Test Pricing
|
Lists the available development and test prices for a product. Dev/Test pricing applies only when you run resources within an Azure subscription that is based on a Dev/Test offer.
|
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) calculator:
If you are starting to migrate to the cloud, a useful tool you can use to predict your cost savings is the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) calculator. This helps in comparing on-premise vs cloud cost.
Azure Tags:
You apply tags to your Azure resources, resource groups, and subscriptions to logically organize them into a taxonomy. Each tag consists of a name and a value pair.
Azure Reservations:
Azure Reservations help you save money by committing to one-year or three-year plans for multiple products. Committing allows you to get a discount on the resources you use. Reservations can significantly reduce your resource costs up to 72% on pay-as-you-go prices. Reservations provide a billing discount and don't affect the runtime state of your resources. After you purchase a reservation, the discount automatically applies to matching resources.
Azure Advisor:
A free service built into Azure that provides recommendations on
- high availability
- security
- performance
- operational excellence
- cost
Azure Cost Management:
Built-in Azure tool that can be used to gain greater insights into where your cloud money is going. You can see historical breakdowns of what services you are spending your money on and how it is tracking against budgets that you have set. You can set budgets, schedule reports, and analyze your cost areas.
Support plans:
Knowledge Center:
Repository for answers to common questions.
Azure Service Level Agreements:
The Service Level Agreement (SLA) describes Microsoft’s commitments for uptime and connectivity.
Understand service-level agreements
- Composite SLAs - Composite SLAs involve multiple services supporting an application, each with differing levels of availability.
- SLAs for multiregion deployments - SLAs for multiregion deployments involve a high-availability technique to deploy the application in more than one region and use Azure Traffic Manager to fail over if the application fails in one region.
Public preview:
The service is in public beta and can be tried out by anyone with an Azure subscription. You can often use these services at a discount as long as they are in preview.
Private preview:
The service is available to specific Azure subscribers for evaluation purpose.
General Availability (GA):
The service is in production and can be used by anyone with an Azure subscription.
Hope these notes will be helpful. Good luck to people attempting the exam!!
Hope these notes will be helpful. Good luck to people attempting the exam!!
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Really good.
ReplyDelete